Sleep apnea involves the breathing airway collapsing periodically during sleep, resulting in a troubled and less productive rest. 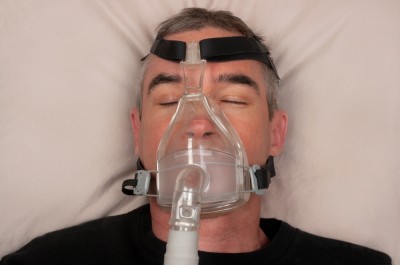
Now, a new study of 34,100 people tracked over an 11-year period shows that sleep apnea patients are more likely to develop pneumonia, a serious inflammation of the lungs that can lead to death.
The researchers behind the study, which was carried out in Taiwan, found that 9.4 per cent of those who suffered from sleep apnea developed pneumonia within a five-year window. In comparison, only 7.8 per cent of those without sleep apnea developed pneumonia over that same period.
“This study showed that sleep apnea is an independent risk factor for incident pneumonia,” noted the researchers, who recently reported their findings in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
The study also found that people who had severe sleep apnea conditions were more likely to develop pneumonia than people with mild sleep apnea symptoms.
So, what’s the connection between sleep apnea and pneumonia?
Researchers suggest that sleep apnea’s impact on the immune system may make patients more vulnerable to the pathogens that can eventually lead to pneumonia.
Sleep apnea can be treated using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device, which is designed to keep the airway from collapsing and disturbing rest.
It’s estimated that between 17 and 24 per cent of all North American adults suffer from some kind of obstructive sleep apnea. Between 2 and 6 per cent of all adults suffer from a severe case of the condition.
Source: Activebeat
